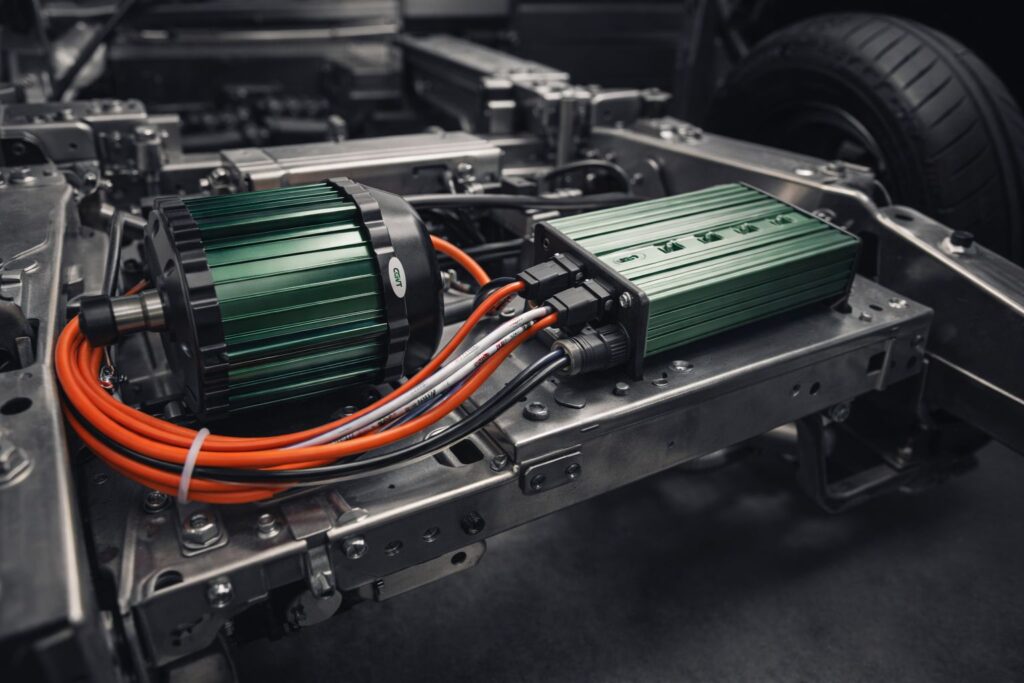
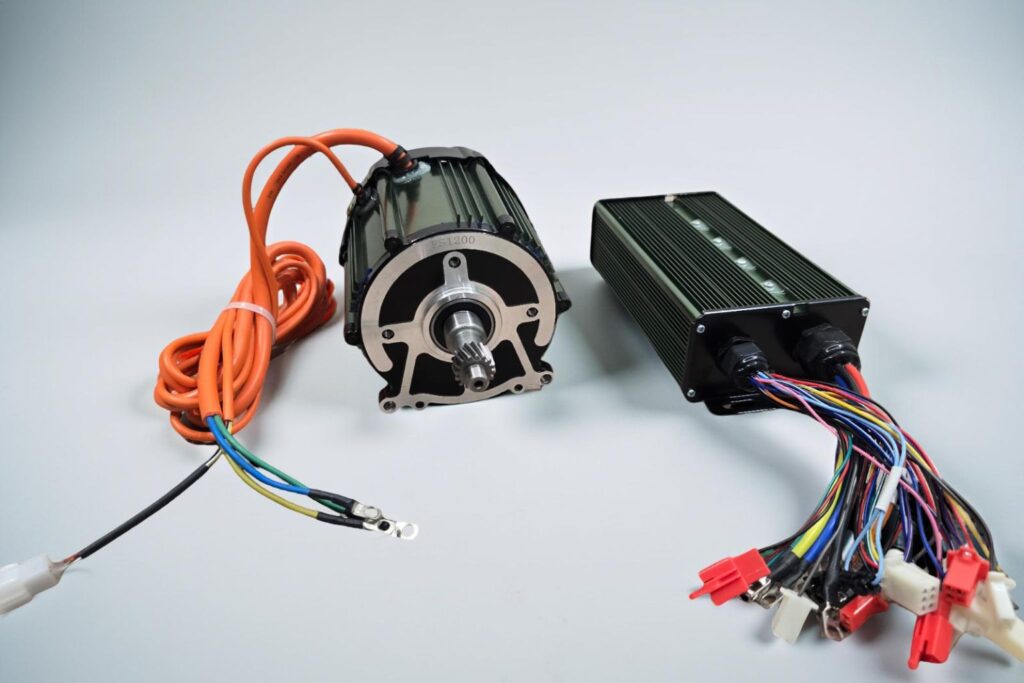
The electric vehicle revolution is reshaping the automotive landscape, promising cleaner transportation and reduced dependence on fossil fuels. Yet beneath the sleek exteriors and silent acceleration lies a complex ecosystem of components working in precise harmony to deliver the efficiency that makes EVs viable. At the heart of this system are two critical elements: electric motors and motor controllers. Understanding how these components function and why their quality matters is essential to appreciating the true potential of electric mobility.
The Foundation of EV Efficiency
Electric vehicles have captured the imagination of consumers and policymakers alike, largely due to their remarkable efficiency advantages over internal combustion engine vehicles. While traditional gasoline engines convert only about 20-30% of the fuel’s energy into actual movement, electric motors can achieve efficiency ratings of 85-95%. This dramatic difference isn’t merely a product of different energy sources; it’s a testament to superior engineering and the fundamental physics of electric propulsion.
However, not all electric motors and controllers are created equal. The quality, design, and integration of these components can mean the difference between an EV that merely meets expectations and one that exceeds them in every meaningful metric, from range and acceleration to longevity and operating costs.
Electric Motors: The Powerhouse of Performance
The electric motor serves as the direct replacement for the internal combustion engine, but the comparison ends there. Unlike engines with hundreds of moving parts requiring precise timing and lubrication, electric motors achieve motion through electromagnetic principles with minimal friction and maximal efficiency.
Types of EV Motors and Their Efficiency Profiles
Modern electric vehicles primarily use three types of motors: permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM), induction motors, and switched reluctance motors. Each offers distinct advantages in terms of efficiency, cost, and performance characteristics.
Permanent magnet motors, which use rare-earth magnets to create a constant magnetic field, are currently the efficiency champions. High-quality PMSM motors can maintain efficiency above 95% across a broad range of operating conditions. The magnets eliminate the need for electrical current to generate the rotor’s magnetic field, reducing energy losses that would otherwise appear as waste heat. Premium manufacturers invest heavily in optimizing magnet placement, rotor geometry, and lamination design to squeeze every percentage point of efficiency from these motors.
Induction motors, popularized by certain high-profile EV manufacturers, take a different approach. While they typically offer slightly lower peak efficiency than permanent magnet motors (around 90-93%), they compensate with exceptional reliability, lower material costs, and freedom from rare-earth supply chain constraints. High-quality induction motors achieve their efficiency through precision manufacturing of rotor bars, careful design of air gaps between rotor and stator, and advanced cooling systems that allow sustained high-power operation without thermal degradation.
How Motor Quality Impacts Real-World Efficiency
The difference between a premium motor and a mediocre one becomes apparent in real-world driving conditions. High-quality motors excel in several critical areas that directly translate to improved efficiency and range.
First, superior materials make an enormous difference. The electromagnetic steel laminations that form the motor’s core significantly influence efficiency. Premium motors use high-grade electrical steel with specific silicon content and grain orientation that minimizes eddy current losses and hysteresis losses. These microscopic energy losses, when multiplied across millions of magnetic cycles, can account for several percentage points of overall efficiency.
Second, precision manufacturing ensures optimal air gaps between rotating and stationary components. Even variations of a few hundredths of a millimeter can increase magnetic reluctance, forcing the motor to work harder and consume more energy to produce the same torque. Quality manufacturers maintain tolerances measured in microns, ensuring that magnetic fields interact with maximum effectiveness.
Third, advanced cooling systems enable motors to maintain peak efficiency across demanding operating conditions. When motors overheat, their resistance increases and magnets can lose strength, both reducing efficiency. High-quality motors incorporate sophisticated liquid cooling channels, thermal management sensors, and materials engineered to dissipate heat rapidly, allowing them to sustain high performance without efficiency degradation.
Motor Controllers: The Brain Behind the Brawn
If the motor is the muscle of an electric vehicle, the motor controller is undoubtedly its brain. This sophisticated piece of electronics manages the precise flow of electrical energy from the battery to the motor, translating driver inputs into smooth, efficient motion. The controller’s role in overall vehicle efficiency is often underestimated, yet it can account for efficiency differences of 5-10% between vehicles with otherwise similar specifications.
The Science of Power Conversion
Motor controllers must perform a remarkably complex task thousands of times per second: converting direct current from the battery into precisely timed alternating current that drives the motor. This process, known as inversion, relies on power electronics components called IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) or, increasingly, silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs.
Every time these switches turn on and off, they experience switching losses, where a small amount of energy dissipates as heat rather than reaching the motor. High-quality controllers minimize these losses through several strategies. Premium silicon carbide components can switch faster and with lower resistance than traditional silicon-based electronics, reducing switching losses by 50% or more. This translates directly into extended range, as more battery energy reaches the wheels rather than heating the power electronics.
Advanced Control Algorithms
Beyond hardware quality, the software algorithms running on the motor controller profoundly impact efficiency. High-end controllers employ sophisticated techniques like field-oriented control (FOC) and model predictive control to optimize motor operation in real-time.
Field-oriented control allows the controller to independently manage the motor’s torque-producing and flux-producing currents, much like a pilot controls an aircraft’s pitch, roll, and yaw independently. This separation enables the controller to minimize reactive current, which circulates in the motor without producing useful work. By maintaining only the precise current needed for the driver’s demanded torque, premium controllers reduce resistive losses in both the motor windings and the controller itself.
Model predictive control takes this further by anticipating optimal control strategies based on predicted future states. If the vehicle is approaching a corner where regenerative braking will be employed, an intelligent controller can subtly adjust motor operation to maximize the energy recovery during deceleration. These marginal gains accumulate over thousands of acceleration and deceleration cycles, meaningfully extending vehicle range.
Regenerative Braking Optimization
One of the defining advantages of electric vehicles is regenerative braking, where the motor acts as a generator during deceleration, converting kinetic energy back into electricity stored in the battery. The efficiency of this process depends almost entirely on the motor controller’s capabilities.
High-quality controllers can recover 60-70% of the kinetic energy during typical braking events, compared to 40-50% for basic systems. This difference stems from several factors: faster response times to driver inputs, more precise control of motor torque during the transition between regenerative and friction braking, and sophisticated algorithms that maximize energy recovery while maintaining smooth, predictable vehicle behavior.
Premium controllers also feature adaptive regenerative braking that adjusts recovery strength based on battery state of charge, temperature, and driving conditions. When the battery is cold or fully charged, aggressive regeneration could damage cells or waste energy as heat. Quality systems modulate regenerative intensity to protect battery health while still recovering maximum usable energy.
The Synergy of System Integration
While individual component quality matters enormously, the true efficiency gains come from how well motors and controllers work together as an integrated system. This integration represents the frontier of EV engineering, where manufacturers differentiate themselves through holistic system optimization.
Thermal Management Harmony
Heat is the enemy of efficiency in electric vehicles. Motors generate heat through resistive and magnetic losses, controllers produce heat through switching and conduction losses, and both must operate within strict temperature ranges to maintain performance. Premium EV systems integrate motor and controller cooling into unified thermal management systems that optimize heat rejection across the entire powertrain.
By sharing cooling loops and control strategies, integrated systems can pre-cool components before demanding acceleration, use waste heat from one component to warm another during cold starts, and maintain all elements within their peak efficiency temperature bands. Studies have shown that sophisticated thermal integration can improve overall powertrain efficiency by 3-5% compared to separately optimized components.
Voltage Optimization
The voltage at which motors and controllers operate significantly influences efficiency. Higher voltages enable lower currents for the same power level, reducing resistive losses in cables, connectors, and semiconductor switches. Leading EV manufacturers have progressively increased system voltages from 400V to 800V and even higher.
However, this voltage increase demands that motors and controllers be specifically designed to operate at these elevated levels. Premium motors feature enhanced insulation systems, precisely wound coils that minimize voltage stress points, and corona-resistant materials that prevent electrical breakdown. High-quality controllers incorporate voltage-appropriate semiconductors, multilayer insulation, and protection circuits that safely handle higher voltages without efficiency-sapping safety margins.
Real-World Impact on Range and Performance
The efficiency improvements from premium motors and controllers translate directly into tangible benefits that EV owners experience daily. Every percentage point of efficiency improvement effectively extends vehicle range without adding battery capacity, weight, or cost.
Consider a vehicle with a 75 kWh battery pack. If upgrading from standard components with 85% combined efficiency to premium components with 92% efficiency, the effective usable energy increases from 64 kWh to 69 kWh. At a typical consumption rate of 250 Wh/mile, this represents an additional 20 miles of range, nearly 10% improvement without changing the battery whatsoever.
Moreover, efficiency improvements reduce thermal stress on all components, extending their operational lifespan. Motors and controllers operating at higher efficiency generate less waste heat, reducing thermal cycling and material degradation. This translates into EVs that maintain their performance characteristics longer, with less range degradation over the vehicle’s lifetime.
The Economics of Quality Components
While premium motors and controllers command higher initial costs, their efficiency advantages create compelling economic arguments over a vehicle’s lifecycle. Reduced energy consumption directly lowers operating costs, and improved component longevity decreases maintenance requirements and extends vehicle value retention.
For fleet operators and commercial vehicles, these advantages become even more pronounced. Vehicles operating for hundreds of thousands of miles can see dramatic total cost of ownership reductions through modest efficiency improvements. A delivery van averaging 100 miles daily and consuming 300 Wh/mile uses about 11,000 kWh annually. Improving efficiency by just 5% saves 550 kWh yearly—at typical commercial electricity rates, this represents hundreds of dollars in annual savings, multiplied across entire fleets.
Looking Toward the Future
The evolution of EV motor and controller technology continues to accelerate. Emerging technologies promise even greater efficiency gains in coming years. Silicon carbide power electronics are becoming mainstream, with next-generation gallium nitride devices showing potential for further switching loss reductions. Novel motor designs incorporating improved cooling integration, advanced magnetic materials, and optimized geometries continue pushing efficiency boundaries.
Machine learning algorithms are beginning to optimize motor control strategies in real-time, adapting to individual driving patterns and environmental conditions to maximize efficiency for each specific journey. As these technologies mature, the efficiency gap between premium and standard components will likely widen, making component quality an even more critical factor in EV competitiveness.
Conclusion
The efficiency of electric vehicles represents one of their most compelling advantages, but this efficiency is far from automatic. It results from careful engineering, quality materials, and sophisticated integration of motors and controllers working in harmony. High-quality components deliver measurable improvements in range, performance, longevity, and operating costs—benefits that compound over a vehicle’s lifetime.
As consumers increasingly embrace electric mobility, understanding the role of these critical components empowers more informed purchasing decisions. Whether choosing between EV models or considering aftermarket upgrades, recognizing that all motors and controllers aren’t created equal helps buyers prioritize vehicles engineered for maximum efficiency.
The transition to electric transportation represents more than a change in fuel source; it’s an opportunity to fundamentally rethink how we approach vehicle efficiency. With premium motors and controllers forming the foundation of this efficiency, the electric vehicles of today and tomorrow stand poised to deliver on the promise of cleaner, more efficient transportation for all.